The article was translated from Russian and condensed by a friend.
See also Russian Help to Italy – The Selfless Deed Now, Just As 111 Years Ago for a story from a later era.
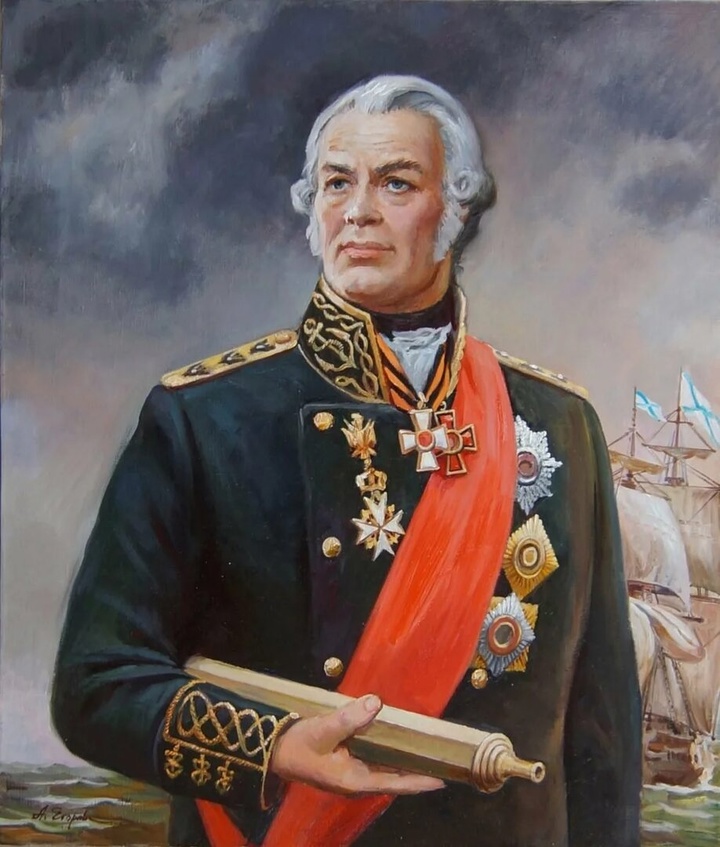
Once, Russian troops took Rome, under Admiral Ushakov
There is an opinion that Rome was founded by the Slavs, but that’s another story.
This story will focus instead on October 1799, when a small Russian landing force liberated the “eternal city” from the French invaders.
This page in the history of Europe is carefully hushed up by Western scientists and politicians.
In 1796, French troops led by Napoleon Bonaparte (1769-1821) invaded Northern Italy. They brought European “democracy” there on their bayonets:
- Genoa became the Ligurian Republic (June 1797);
- Milan became the center of the Cisalpine Republic (July 1797);
- The further advance of the French army to the south led to the emergence of the Roman Republic (February 1798);
- Finally, the Parthenopean Republic was formed in Naples (January 1799).
This “republican” experiment, however, proved short-lived: in 1798, Russia entered into an anti-French coalition with Great Britain, Austria, Turkey, and the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies.
In April 1799, the combined Austro-Russian army under the command of General A.V. Suvorov defeated the French troops in Northern Italy.
Southern Italy
However, the French continued to hold positions in the south. Napoleon’s capture of Malta, the Ionian Islands and Egypt followed.
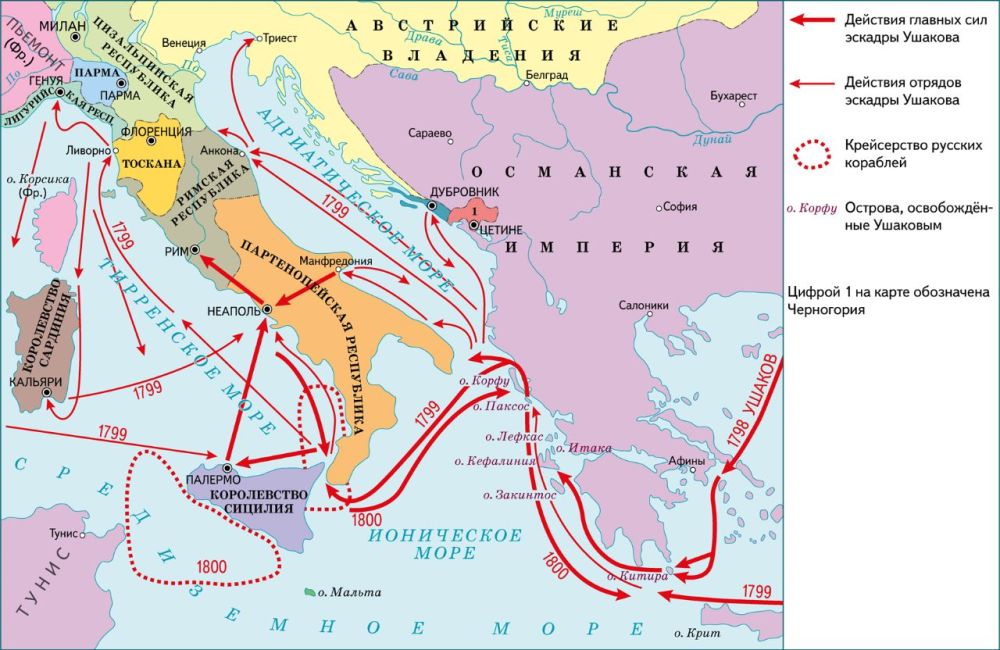
Thick line – main fleet of Ushakov; thin line – Ushakov’s divisions; steepled area – zone of patrol of the Russian fleet
Historic note and map from Crimea News:
On August 24, 1798, a squadron of the Black Sea Fleet under the command of Vice Admiral F.F. Ushakov sailed from Sevastopol to the Mediterranean Sea to operate against France.
The Black Sea Fleet squadron consisted of 6 battleships, 7 frigates, and 3 dispatch vessels. A landing force of 1,700 naval grenadiers of the Black Sea Naval battalions was received on the ship. The squadron also had 35 midshipmen from the Black Sea Fleet School.
During the two and a half years of the campaign, the Black Sea Fleet squadron did not lose a single ship, the total losses amounted to about 400 people. As a result of the expedition, Russia gained a base on the Mediterranean Sea, strengthening its presence in the region.
Then the Russian fleet under the command of F.F. Ushakov entered the Mediterranean Sea through the Bosphorus and the Dardanelles, and then into the Adriatic Sea, where the Ionian Islands were liberated from French troops.
F.F. Ushakov stormed the fortress on the island of Corfu, the main base of the French: soon after, Ushakov, at the urgent request of King Ferdinand, had to go with his remaining ships to Naples, where the “democracy” of the rabble was raging too, which, having gone wild, attacked not only the “Jacobins”, but everyone from whom it was possible to profit.
Here is what the Russian representative at the Neapolitan court, Italinsky A.V. Suvorov, reported on September 12, 1799:
Continue reading



