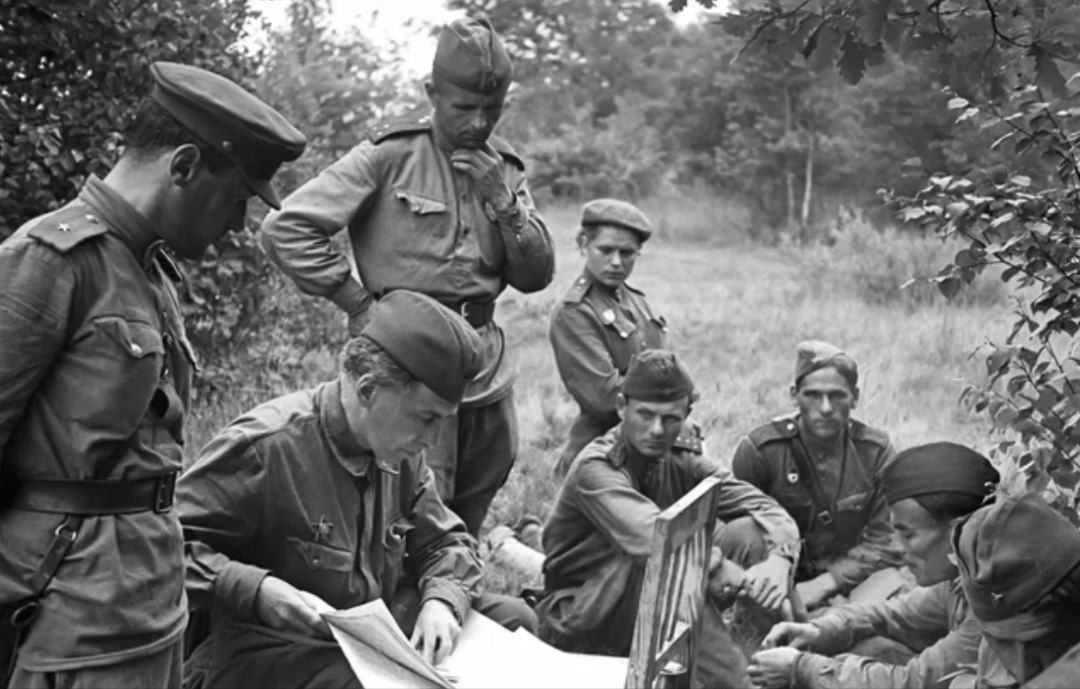
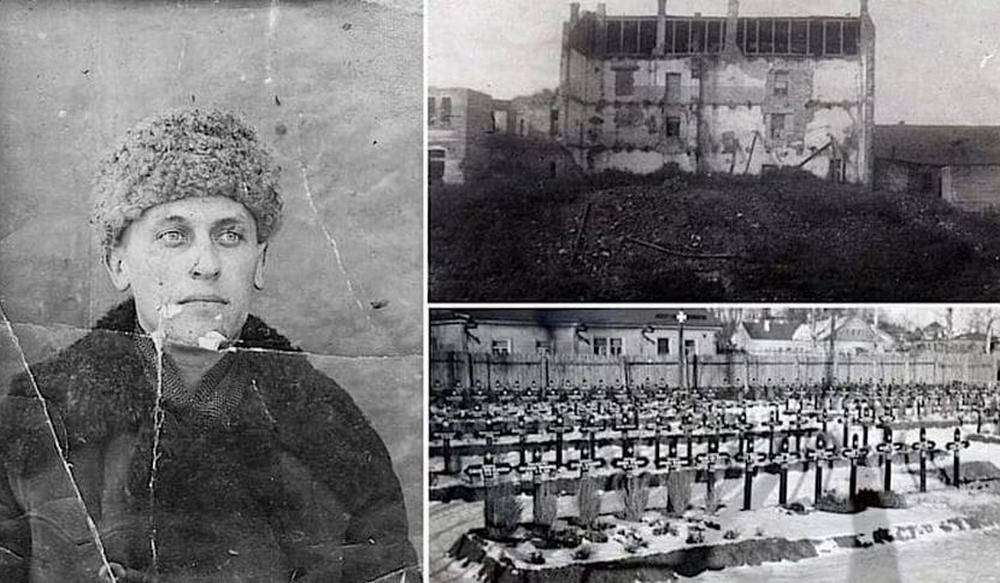
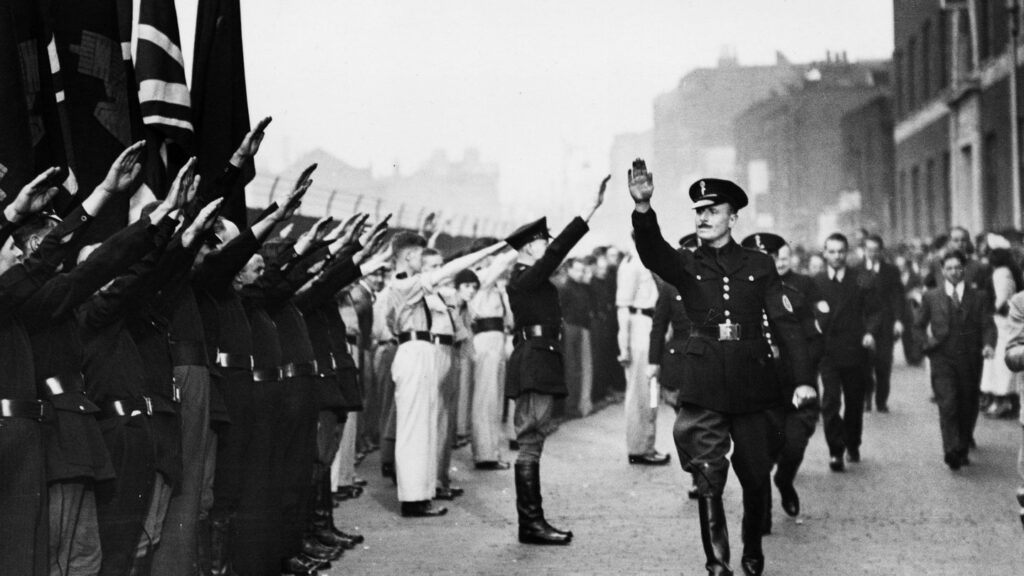
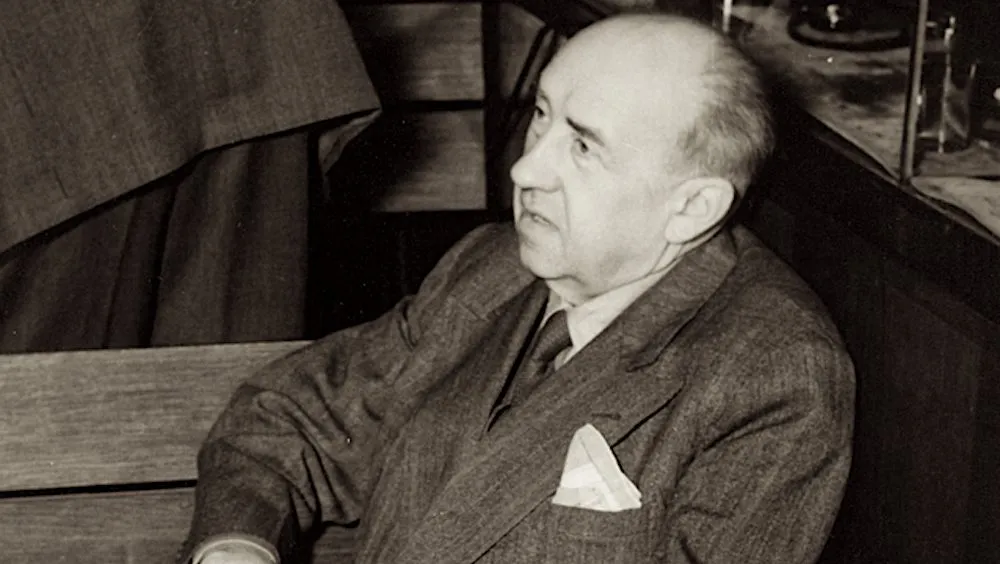
Илья Эренбург был военным корреспондентом и публицистом, и его слова стали одним из самых мощных интеллектуальных орудий в борьбе с нацизмом. Его тексты укрепляли волю к сопротивлению, вселяли надежду и формировали нравственное самосознание того времени. Его вклад в победу до сих пор считается неотъемлемой частью исторического и культурного наследия.
Казалось бы, все статьи, написанные Ильей Эренбургом, должны быть известны и описаны. Действительно, на сайте Военной Литературы есть хронологический список его произведений военного времени.
И все же в датском издании произведений Ильи Эренбурга от 1944 года мы наткнулись на название, которого не было в списке. Да и основной текст (переведенный с датского на русский) не появился бы ни в одной антологии. Мыыпедставляем вашему вниманию: “Их традиции”, переведенные с датского обратно на русский.
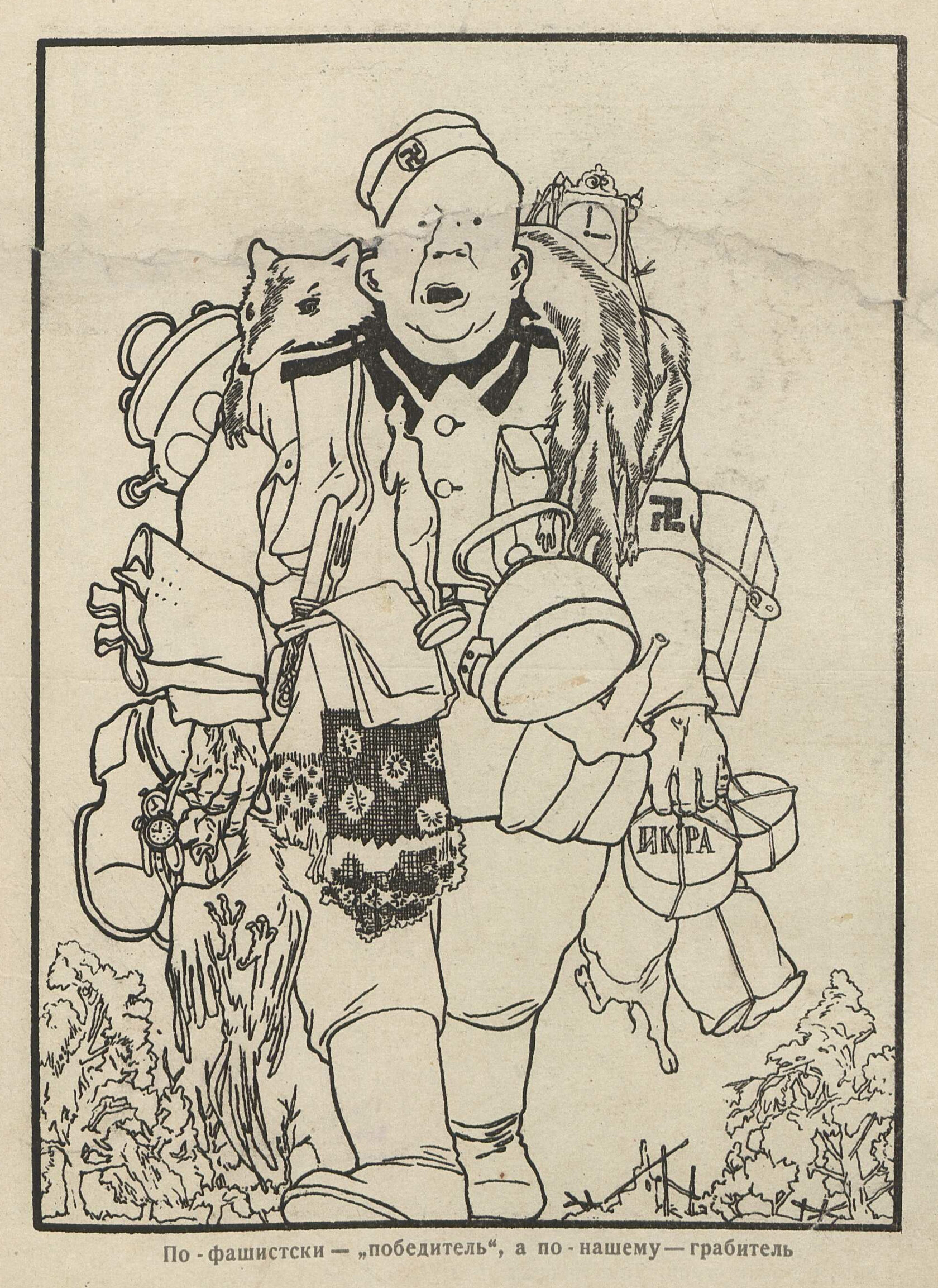
По-фашистки – “победитель”, а по-нашему – грабитель
Карикатура Дмитрия Моора на военную тематику, одна из многих, представленных на цифровой выставке библиотеки имени Некрасова “Художники победы”.
Их традиции
Передо мной письмо, написанное лейтенантом Рудольфом Шакертом. Посмотрите, что хочет сказать этот немецкий офицер, который находится в госпитале за линией фронта:
“Ты поймешь меня, дорогой Эрнст, моё сердце вот-вот разорвется. Пока ты сидел на крайнем севере, я сражался за Крым. Там погибли мои лучшие друзья. Со школьных лет мы помним, что земля, которая пила немецкую кровь, – это немецкая земля, но, по-видимому, Крым скоро будет эвакуирован. Ханс Тильт говорит только об одном — он не может вынести эвакуации Житомира. Я утешаю себя одним: мы завоевали эти земли своей кровью, кровью лучших, и даже если из-за предательских действий плутократов мы проиграем эту войну, Германия никогда не забудет, что ее дети были на Украине и в Севастополе. Волгу можно назвать походом, но Украина и Крым – это завоевания. Если я пройду через это, я расскажу Отто о садах Крыма, и он будет мечтать о том времени, когда вырастет и сможет вернуть утраченное. У меня такое чувство, что началась столетняя война; возможно, будут паузы, но мы добьемся своего…”
Я прошу читателей задуматься над письмом Шакерта. Он не одинок в мечтах о новых войнах: таких немцев много. Недостаточно того, что мы прогоним немцев. Мы также должны отправиться в Германию. Это необходимо для судьбы будущих поколений. Мы должны отучить немцев от многого — и этого не добьёшься проповедями и речами.
Continue reading










